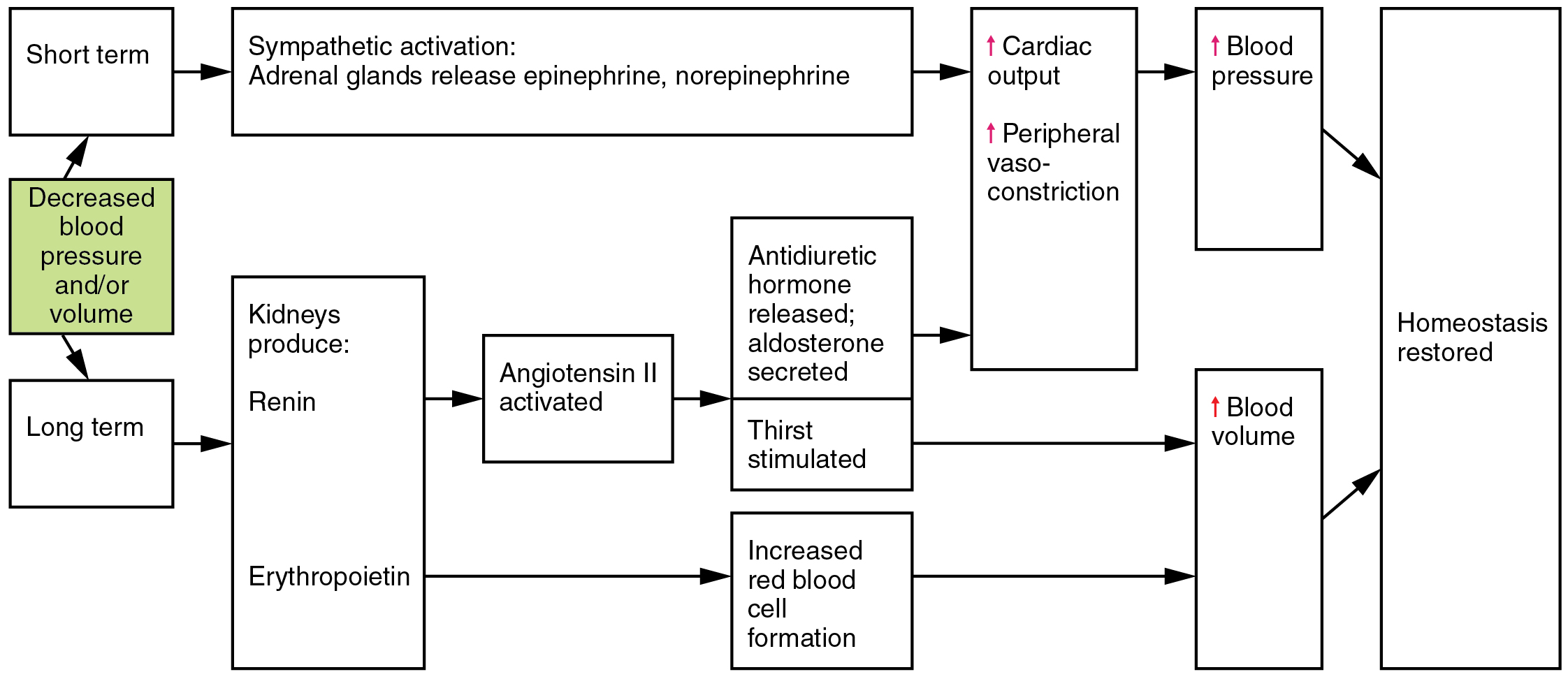
Flow Chart Upon Immediate Standing Of Cardiac

Congestive heart failure (CHF) otherwise known as cardiac failure refers as the inability of the heart to pump sufficient blood to meet needs of tissues for oxygenation and nutrition. This disease can affect the heart’s ability to respond to circulation demands of the body. CHF is a slowly developing condition where cardiac output is lower-than-normal.PathophysiologyIn CHF, the contractile properties of the heart are impaired. This leads to a decreased cardiac output. Cardiac output (CO) is best described by the equation CO = HR (heart rate) x SV (stroke volume). Heart rate is an autonomic nervous system function and in cases where CO falls, sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate to maintain adequate cardiac output.
When the compensatory mechanism fails to maintain adequate tissue perfusion, the properties of stroke volume must adjust to maintain CO. But if the main problem in CHF is the damage of heart muscle fibers, stroke volume is impaired and CO cannot be maintained to normal output.The amount of blood pumped in each contraction is what you call the stroke volume (SV). SV is dependent on three factors namely the preload which is the volume of blood filling the heart.
Amount of blood brought to the heart is directly proportional to the pressure applied by the length of stretch of the myocardial fibers. The second factor relating to stroke volume is the changes in the force of contraction occurring at the cellular level which is termed as contractility. This factor is related to the length of myocardial fibers and the levels of calcium in the body. The third factor is referred to as afterload. This is the amount of pressure of ventricles needs to come up to be able to pump blood across the pressure gradient that is created with the arteriole resistance.
Text in this Example: Blood Flow through the Heart Source: U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health and Human Services. Www.fda.gov Inferior vena cava brings blood from the legs and the lower part of the body Superior vena cava brings blood from the head, neck, and arms Blood from the body is carried into.
Etiology of CHFMyocardial Weakness. Common cause of myocardium weakness is ischemia related to Atherosclerosis and its stenosis of the coronary arteries. When stenosis reaches about 50-70%, only resting myocardial oxygen can be met. When atherosclerosis progresses myocardial fibers undergo hypoxic injury leading to necrosis.
These fibers are then replaced with fibrous connective tissue resulting to deteriorating pumping capacity of the heart and reduced ventricular compliance. Other myocardial ischemia cause is thrombosis in the coronary arteries. Myocardial weakness can developed with myocarditis or cardiomyopathies.Restrictions to PumpingSome physical factors restrict the heart’s pumping ability such as malfunction in cardiac valve. Inability of the valves to open widely causes decreased blood flow to the heart leading to a reduced cardiac output. Congenital Heart Defects also restrict the pumping of the heart by interfering the free flow of blood in myocardium. Presence of mass (may be a thrombus or tumor) within cardiac chamber can cause internal obstruction by occupying a portion of chamber’s volume, thereby reducing the chamber’s blood capacity.
The most common cardiac tumor, myxoma, is of endothelial origin and is most often located at the left atrium. This type of tumor accounts for 35-50% of all primary cardiac tumors. Its presence can occlude mitral valve which can cause instant death or can serve as a site for the formation of thromboembolus. Pumping may also be restricted by cardiac dysrhythmias, pericarditis and cardiac tamponade.Increased AfterloadInability to maintain cardiac output may also result from overload. In cases where the myocardium is constantly exposed to high physical demand, the strain may overwhelm the heart and the result is declined contractility and stroke volume which is likely seen when cardiac afterload is increased. The right ventricle faces this type of situation in certain lung diseases such as Cor Pulmonale where vascular damage causes pulmonary hypertension. Systemic hypertension can also increase afterload as elevated BP presents an increased resistance that the left ventricle must overcome to maintain an adequate CO.
Furthermore, valve disease or congenital defects in the cardiac outflow tracts, valves, pulmonary trunk or aorta can also produce excessive ventricular afterload. Congestive Heart failure PathophysiologySchematic Diagram Credits: Pathophysiology, Concepts and Applications for Health Care Professionals by Thomas J. Gordon Hanford, 3rd EditionPathogenesisTwo significant factors are considered when congestive heart failure pathophysiology is discussed. First, the heart is unable to clear itself with of the delivered blood.
The second factor is how long it takes for the signs and symptoms to develop.In this pathophysiology explanation, we will use mitral stenosis as the etiologic factor of CHF. Stenosis of the mitral valve produces hardened and thicker valve cusps that cannot fully open. This decreases the passageway of blood from the left atrium to left ventricle. The stenosed portion interferes with ventricular filling leading to decline in stroke volume and cardiac output.
When stenosis increases, cardiac output may even fail to meet demands even at rest. As a result the affected individual experiences weakness, fatigue and fainting.When blood cannot easily flow, it backs into the right atrium and then to the lungs.

Flow Chart Upon Immediate Standing Of Cardiac System
Pulmonary congestion in return produces pulmonary hypertension with pressure sometimes rising 3-5 times above normal. With high pressure, fluid accumulates in the lung interstitium, otherwise known as pulmonary edema which stiffens lungs making it less elastic and more firm. Fluids are forced from pulmonary tissues to alveolar air spaces as the condition progresses. When fluids accumulate in alveoli and bronchioles, surface for diffusion is reduced resulting to airway obstruction and manifested as difficulty of breathing or dyspnea.In congestive heart failure, dyspnea is aggravated when lying down, a condition called orthopnea. The cause of orthopnea is the increased load placed on the failing heart.
This pulmonary burden adds more pulmonary congestion, edema and aggravation of respiratory difficulty. Orthopnea is managed by assisting the individual to sitting or fowler’s position.Patient’s diagnosed with CHF report bouts of dyspnea at nighttime.
This condition is referred as paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea. Unlike orthopnea, relied is not quickly achieved by sitting down. About 30 minutes in an upright position is needed for breathing to become easier.Aside from breathing difficulties, pulmonary hypertension can also cause aneurysms in small pulmonary vessels which may rupture and cause hemorrhage in the lungs. Pulmonary hypertension and congestion can lead to secondary infection.
A common complication of CHF is bronchopneumonia.As CHF progresses, backup of blood in the right heart can increase the right heart’s preload. The right responds with hypertrophy that increases their strength and enables them to compensate with an increased stroke volume.
This results to an enlarged heart which is called cardiomegaly. Cardiomegaly characterizes a chronically failing heart.When the right heart congestion develops, systemic venous congestion results manifested by swelling of the major superficial veins. Often clients with CHF are noted with swelling jugular veins. With elevation of systemic venous pressure, capillary pressures also increased leading to systemic edema.
Following the pull of gravity fluid accumulation in the lower parts of the body are noticed in ankles when the person is sitting or standing, a condition termed as dependent edema.Systemic edema also has significant effects on the liver and spleen. Blood congested in the liver causes it to enlarged, a condition known as hepatomegaly.
Congestion of blood in the hepatic system produces high pressures that can damage hepatocytes or cause the vessels to rupture resulting to hemorrhage.Hepatic system hypertension may also cause back pressure leading to spleen congestion or splenomegaly, which is associated with severe and advanced CHF. Daisy Abastar holds a degree in Bachelor of Science in Nursing. Her work experiences include Nursing Local Board Examination Reviewer, Clinical Instructor, NC2 Examination Reviewer and Caregiver Lecturer. Subjects handled: Psychiatric, Obstetric, Pediatric and Fundamentals of Nursing. She also specialized in these areas: ER, Orthopedic Ward and the DR. In addition to passing NLE, she also passed IELTS examination.
Her written works are combined learning from theoretical to actual nursing background and ongoing research.
Advanced Office Password Recovery 6.22 Full Review: Advanced Office Password Recovery 6.22 Full is very useful application that help users to recover lost or forgotten passwords to files or documents created in Microsoft Office components and other Microsoft software. Download Advanced Office Password Recovery 6.22 Serial Key. Elcomsoft advanced office password recovery pro key.
Part II: Assessment Techniques, Con't.MurmursA heart murmur is a very general term used to describe any one of the verity of abnormal sounds heard in the heart due to turbulent or rapid blood flow through the heart, great blood vessels, and/or heart valves (whether the heart valves are normal or are diseased). Most nurses associate murmurs with an abnormal heart valve. However, there are a variety of other conditions that can cause murmurs. Murmurs can also be caused by the forward flow of blood across a constricted or otherwise irregular valve, or into a dilated heart chamber or dilated vessel.
They can also be caused by the backward flow of blood through an incompetent valve or a septal defect murmurs are usually described as a “rushing” or “swooshing” sound. Murmurs are usually related to defect in valves or ventricular septal defect, or atrial septal defect.When ausculatining murmurs, the nurse should record the timing, characteristics, location, and radiation of the murmur. Characteristics include: loudness, intensity, pitch, and quality of the murmur.
These assessment factors are discussed in more detail later in the course.Gallops:The bell of the stethoscope may be used for low frequency sounds (they are better amplified by the bell). S3 and S4 gallops are generally low-pitched sounds and are heard best with the bell of the stethoscope while the patient is stretched out on his left side. Many nurses prefer to auscultate the heart sounds a second time with the bell of the stethoscope in order to detect any sounds that might be missed with the diaphragm. S3 gallop, the ventricular gallop, occurs at the end of ventricular systole. It is often caused by the sound of blood prematurely rushing into the ventricle that is stiff or dilated due to heart failure, coronary artery disease, or pulmonary hypertension.ClicksSounds described as “clicks” are extra sounds often heard in those patients with mitral valve prolapsed, aortic stenosis, or those with prosthetic heart valves. Opening “snaps” are usually caused by mitral stenosis or stenosis of the tricuspid valves.RubsSounds referred to as “rubs” occur when the visceral and parietal layers of the pericardium rub together.
The sound is produced when inflammation is present due to uremic pericarditis, myocardial infarction, or other inflammatory condition.Discussion of Heart SoundsThe loudness and intensity of heart sounds are important when you are listening. S1 and S2 are heard at different levels of loudness, depending upon where you listen on the chest. The loudness of S1 is mainly determined by the position of the heart valves when ventricles contract. If valve leaflets are wide open at the time of contraction, the sound is very loud.The loudness of the sound is also affected by the pressure of the blood. It is this pressure that “slams” the valves shut and generates the sound. If you recal that the interval between S1and S2 corresponds to the systolic phase, then a murmer that is heard between S1 and S2 wuld be called a systolic murmur. Then a diastolic murmur would be called a murmer heard between S2 and S1, which corresponds to the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle.Next, these two murmurs, systolic and diastolic, can further be pinpointed by descriving exactly when in the phase it occurs.
The murmur can be described as:Early systolicMidsystolicLate systolicEarly diastolicMiddiastolicLate diastolicThese above terms describe murmurs in the exact position that they fall I the phase. For example, an early systolic murmur would be “timed” as occurring early in the phase of systole; and so on for all the phases. Another term called holosystolic (also called pansystolic), is used to describe a murmur heard throughout the entire systolic phase (S1 to S2). Similarly, holodiastolic will be used to refer to the murmur heard throughout the entire diastolic phase (S2 to S1).The timing of the murmur above is very difficult to assess in some patients. In other patients, the timing will be very easy to assess. An important factor is that the nurse has experience in listening to a variety of “normal” variation of normal heart sounds. You must first listen to many different normal heart sounds.
Once you have some experience at differentiating normal S1 and S2 sounds, then you will be able to identify abnormal sounds, and to determine the timing of those abnormal sounds.The valves are sat their widest when blood is actually filling into the ventricle. As the ventricle fills and the atria empty, the leaflets of the valve begin to close or to narrow. At that point, when the atria are empty, the ventricle is contracting, and slams the valve shut.
This is the dynamic force behind the loudness and intensity of the heart sounds.Other factors affect closure. Exercise, fever, anemia, and other factors and affect heart rate and force of the closure of the valves. Loudness, of course, is also affected.